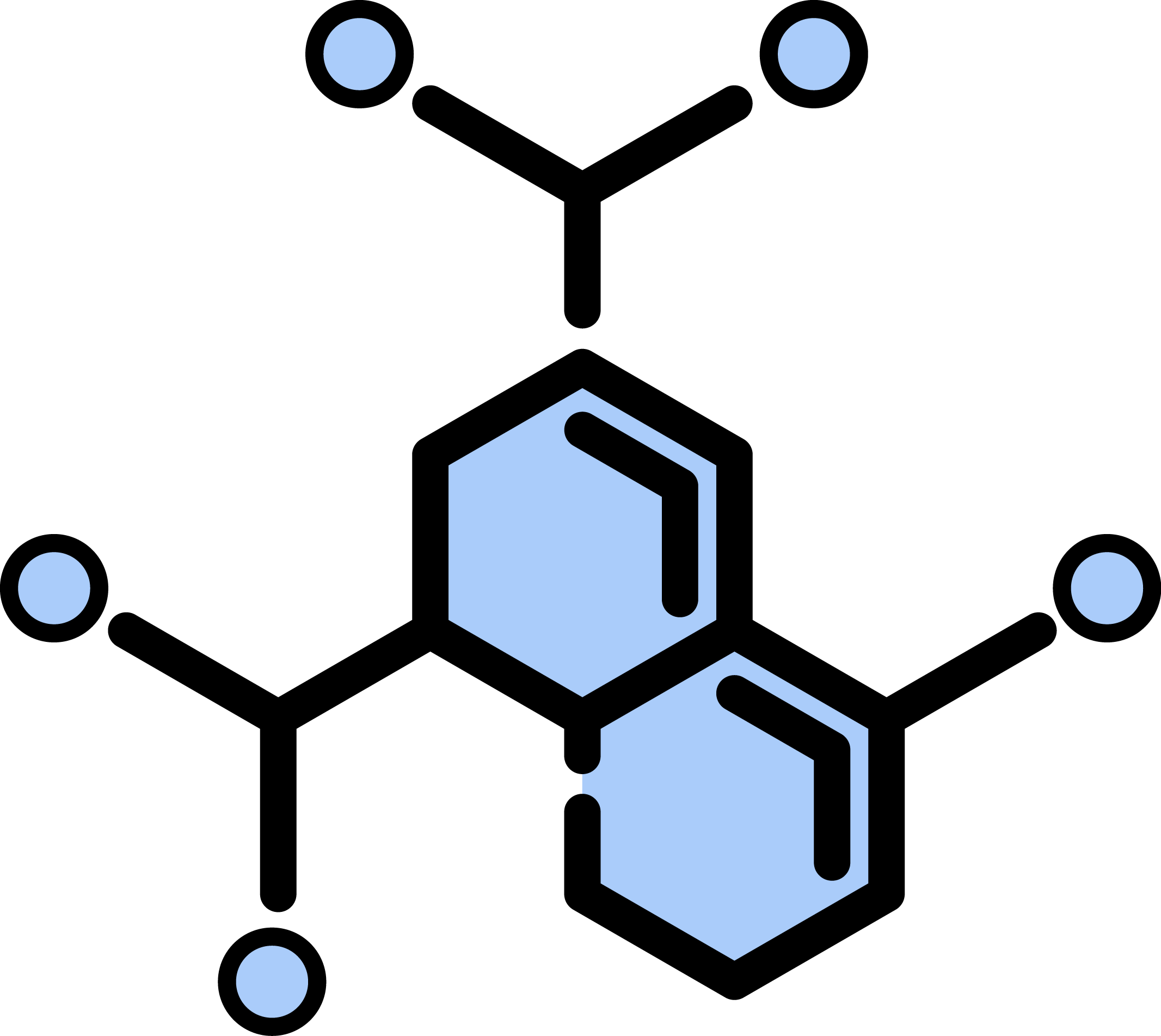
Phosphosite: 185 in P28482
| UniProt ID | P28482 |
|---|---|
| Protein Name |
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAP kinase 1) (MAPK 1) (EC 2.7.11.24) (ERT1) (Extracellular signal-regulat ed kinase 2) (ERK-2) (MAP kinase isoform p42) (p42-MAPK) (Mitogen-activated protein kinase 2) (MAP kinase 2) ( MAPK 2) |
| Gene Name | MAPK1 |
| Position | 185 |
| SequenceWindow | HDHTGFLTEYVATRW |
| Function Score? | 1 |
| Disorder score? | 0.162 Ordered |
| Protein-Targeted Drug | BVD-523; HH2710; ASTX029; LY3214996; VAN-10-4-eluting stent; GDC-0994; JSI-1187; CHIR-99021; COR-D; SB220025; AEZS-131; SCH772984; ERK inhibitor III; (4-Fluoro-phenyl)-(9-methyl-9H-purin-6-yl)-amine; FR-180204; DEBROMOHYMENIALDISINE; Phosphonothreonine; KT-5720; Ro31-8220; Ro-4396686; BMS-536924; KN-62; CI-1040; "4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole"; "4-[(3,5-diamino-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)diazenyl]phenol"; Bisindolylmaleimide-I; RO-316233; Acetylsalicylic acid; Minocycline; Arsenic trioxide; Olomoucine; Phosphonothreonine; Colforsin; Purvalanol; SB220025; Seliciclib; Perifosine; N,N-DIMETHYL-4-(4-PHENYL-1H-PYRAZOL-3-YL)-1H-PYRROLE-2-CARBOXAMIDE; N-BENZYL-4-[4-(3-CHLOROPHENYL)-1H-PYRAZOL-3-YL]-1H-PYRROLE-2-CARBOXAMIDE; (S)-N-(1-(3-CHLORO-4-FLUOROPHENYL)-2-HYDROXYETHYL)-4-(4-(3-CHLOROPHENYL)-1H-PYRAZOL-3-YL)-1H-PYRROLE-2-CARBOXAMIDE; (3R,5Z,8S,9S,11E)-8,9,16-TRIHYDROXY-14-METHOXY-3-METHYL-3,4,9,10-TETRAHYDRO-1H-2-BENZOXACYCLOTETRADECINE-1,7(8H)-DIONE; 5-(2-PHENYLPYRAZOLO[1,5-A]PYRIDI . . . more
|
| Protein Subcellular Localization | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle {ECO:0000250}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32721402}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32721402}. Membrane, caveola {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63086}. Cell junction, focal adhesion {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63085}. Note=Associated with the spindle during prometaphase and metaphase (By similarity). PEA15-binding and phosphorylated DAPK1 promote its cytoplasmic retention. Phosphorylation at Ser- 246 and Ser-248 as well as autophosphorylation at Thr-190 promote nuclear localization. {ECO:0000250}. . . . more
|
| Protein Function | Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 are the 2 MAPKs which play an important role in the MAPK/ERK cascade. They participate also in a signaling cascade initiated by activated KIT and KITLG/SCF. Depending on the cellular context, the MAPK/ERK cascade mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation through the regulation of transcription, translation, cytoskeletal rearrangements. The MAPK/ERK cascade also plays a role in initiation and regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells by phosphorylating a number of transcription factors. About 160 substrates have already been discovered for ERKs. Many of these substrates are localized in the nucleus, and seem to participate in the regulation of transcription upon stimulation. However, other substrates are found in the cytosol as well as in other cellular organelles, and those are responsible for processes such as translation, mitosis and apoptosis. Moreover, the MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of the endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC); as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. The substrates include transcription factors (such as ATF2, BCL6, ELK1, ERF, FOS, HSF4 or SPZ1), cytoskeletal elements (such as CANX, CTTN, GJA1, MAP2, MAPT, PXN, SORBS3 or STMN1), regulators of apoptosis (such as BAD, BTG2, CASP9, DAPK1, IER3, MCL1 or PPARG), regulators of translation (such as EIF4EBP1 and FXR1) and a variety of other signaling-related molecules (like ARHGEF2, DCC, FRS2 or GRB10). Protein kinases (such as RAF1, RPS6KA1/RSK1, RPS6KA3/RSK2, RPS6KA2/RSK3, RPS6KA6/RSK4, SYK, MKNK1/MNK1, MKNK2/MNK2, RPS6KA5/MSK1, RPS6KA4/MSK2, MAPKAPK3 or MAPKAPK5) and phosphatases (such as DUSP1, DUSP4, DUSP6 or DUSP16) are other substra . . . more
|
| Functional domains |
Distribution of Tumor Phosphorylation Levels (corrected without protein) in Pan-Cancer
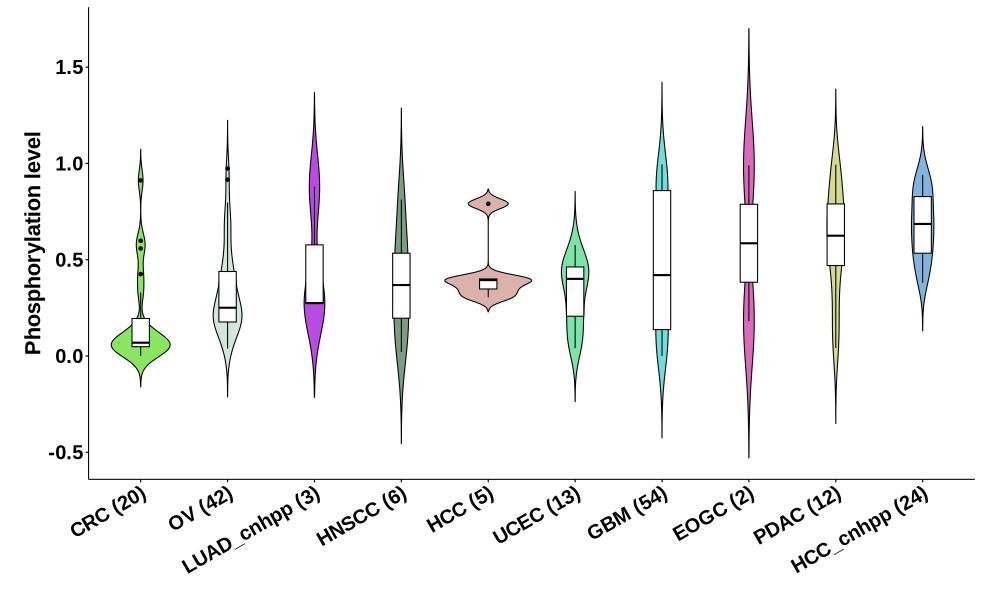
Distribution of Tumor Phosphorylation Levels (corrected with protein) in Pan-Cancer

Distribution of Normal Phosphorylation Levels (corrected without protein) in Pan-Cancer
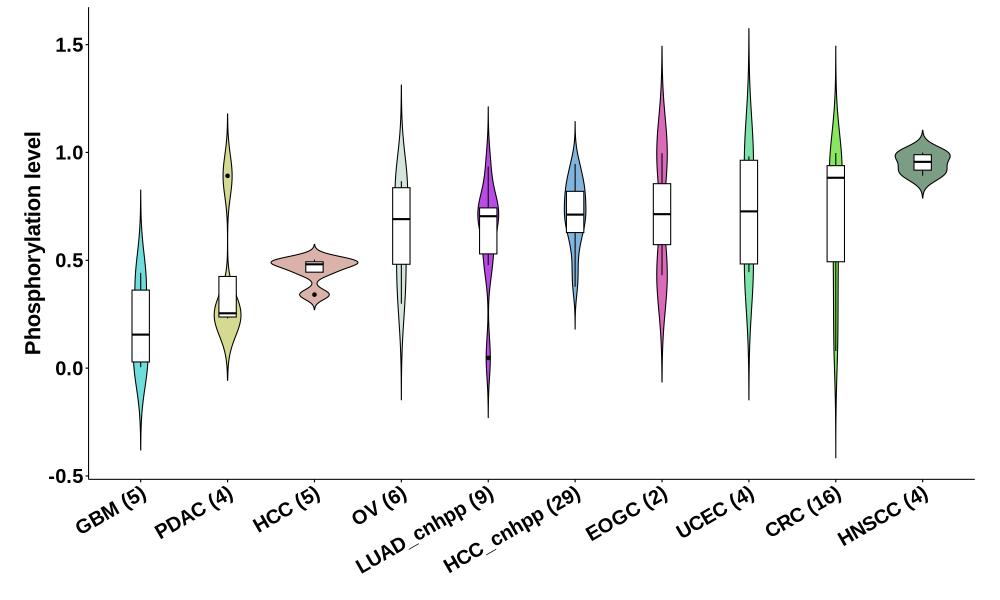
Distribution of Normal Phosphorylation Levels (corrected with protein) in Pan-Cancer

Copyright © Jing Li's group, SJTU. All rights reserved.