Phosphosite: 172 in P54646
| UniProt ID | P54646 |
|---|---|
| Protein Name |
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 (AMPK subunit alpha-2) (EC 2.7.11.1) (Acetyl-CoA car boxylase kinase) (ACACA kinase) (Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase kinase) (HMGCR kinase) (EC 2.7.11.31) |
| Gene Name | PRKAA2 |
| Position | 172 |
| SequenceWindow | SDGEFLRTSCGSPNY |
| Function Score? | 0.999 |
| Disorder score? | 0.261 Ordered |
| Protein-Targeted Drug | Adenosine phosphate; Acetylsalicylic acid; Fostamatinib; CHEMBL:CHEMBL2348411; METFORMIN; METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE; HESPERADIN; ACADESINE; NULL; OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION INHIBITOR IM156; SAPONARIN; VALPROIC ACID; IMEGLIMIN . . . more
|
| Protein Subcellular Localization | Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BRK8}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15866171}. Note=In response to stress, recruited by p53/TP53 to specific promoters. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15866171}. . . . more
|
| Protein Function | Catalytic subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an energy sensor protein kinase that plays a key role in regulating cellular energy metabolism (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). In response to reduction of intracellular ATP levels, AMPK activates energy-producing pathways and inhibits energy-consuming processes: inhibits protein, carbohydrate and lipid biosynthesis, as well as cell growth and proliferation (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). AMPK acts via direct phosphorylation of metabolic enzymes, and by longer-term effects via phosphorylation of transcription regulators (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). Regulates lipid synthesis by phosphorylating and inactivating lipid metabolic enzymes such as ACACA, ACACB, GYS1, HMGCR and LIPE; regulates fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis by phosphorylating acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACACA and ACACB) and hormone-sensitive lipase (LIPE) enzymes, respectively (PubMed:7959015). Promotes lipolysis of lipid droplets by mediating phosphorylation of isoform 1 of CHKA (CHKalpha2) (PubMed:34077757). Regulates insulin-signaling and glycolysis by phosphorylating IRS1, PFKFB2 and PFKFB3 (By similarity). Involved in insulin receptor/INSR internalization (PubMed:25687571). AMPK stimulates glucose uptake in muscle by increasing the translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 to the plasma membrane, possibly by mediating phosphorylation of TBC1D4/AS160 (By similarity). Regulates transcription and chromatin structure by phosphorylating transcription regulators involved in energy metabolism such as CRTC2/TORC2, FOXO3, histone H2B, HDAC5, MEF2C, MLXIPL/ChREBP, EP300, HNF4A, p53/TP53, SREBF1, SREBF2 and PPARGC1A (PubMed:11554766, PubMed:11518699, PubMed:15866171, PubMed:17711846, PubMed:18184930). Acts as a key regulator of glucose homeostasis in liver by phosphorylating CRTC2/TORC2, leading to CRTC2/TORC2 sequestration in the cytoplasm (By similarity). In response to stress, phosphorylates 'Ser-36' of histone H2B (H2BS36ph) . . . more
|
| Functional domains |
Distribution of Tumor Phosphorylation Levels (corrected without protein) in Pan-Cancer
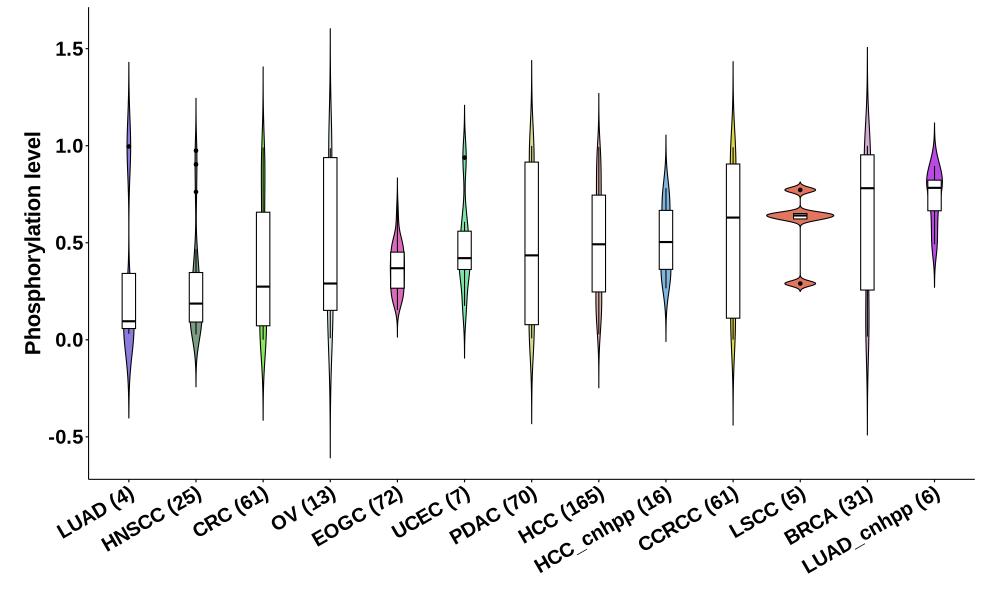
Distribution of Tumor Phosphorylation Levels (corrected with protein) in Pan-Cancer

Distribution of Normal Phosphorylation Levels (corrected without protein) in Pan-Cancer
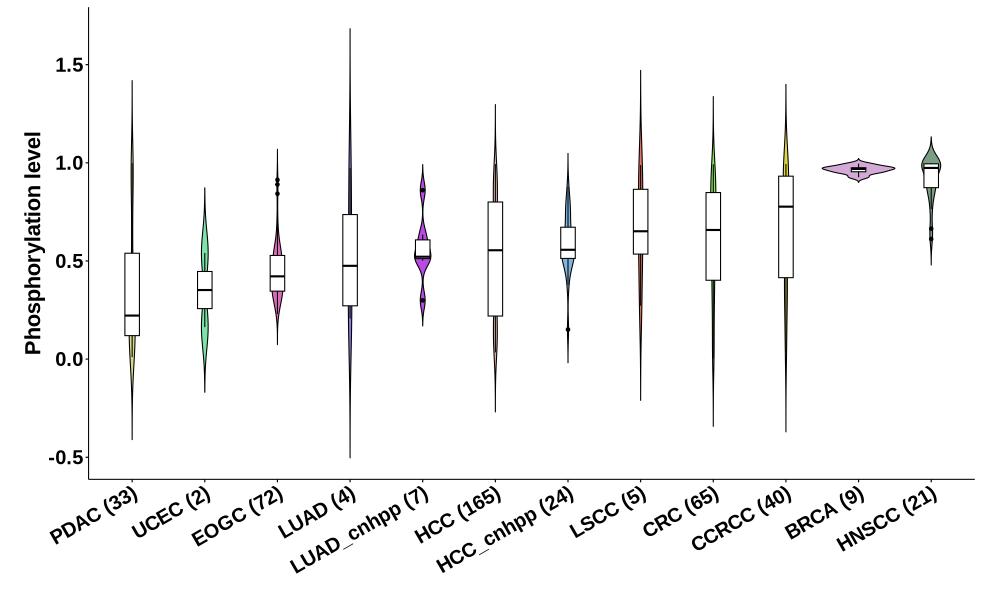
Distribution of Normal Phosphorylation Levels (corrected with protein) in Pan-Cancer

Copyright © Jing Li's group, SJTU. All rights reserved.